Hearing loss is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur at any age and may result from various factors, including genetics, aging, exposure to loud noise, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the types, causes, and prevention strategies for hearing loss can help you maintain optimal hearing health and improve your quality of life.
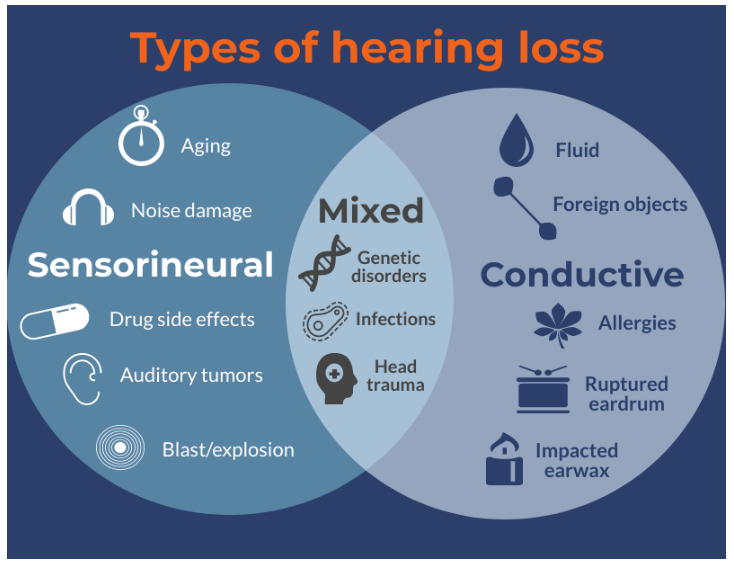
Types of Hearing Loss
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve. It is the most common type of permanent hearing loss and can be caused by aging, exposure to loud noise, genetics, and certain medications.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a blockage or damage to the middle ear or ear canal, preventing sound from reaching the inner ear. Causes may include ear infections, earwax buildup, and abnormalities of the ear structure.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. It can occur when there is damage to both the inner ear and the middle or outer ear.
Auditory Processing Disorders
Auditory processing disorders (APD) are conditions that affect the brain’s ability to interpret and process sounds correctly, even when the ears function normally. People with APD may have difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments.
Causes of Hearing Loss
- Aging: As we age, the structures of the inner ear can deteriorate, leading to age-related hearing loss (presbycusis).
- Loud Noise Exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud noises, such as machinery, music concerts, or firearms, can damage the hair cells in the inner ear, leading to hearing loss.
- Genetics: Some people may inherit genes that make them more susceptible to hearing loss.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as otosclerosis, Meniere’s disease, and tumors, can cause hearing loss.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and high doses of aspirin, can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Prevention of Hearing Loss
- Protect Your Ears: Wear ear protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, when exposed to loud noises.
- Limit Exposure to Loud Noise: Turn down the volume on personal audio devices and avoid prolonged exposure to loud noises.
- Get Regular Hearing Check-ups: Schedule regular hearing screenings with an audiologist to monitor your hearing health and detect any changes early.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing hearing loss due to its harmful effects on blood flow to the ears.
- Treat Medical Conditions: Manage underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease, to reduce the risk of hearing loss.
Conclusion
Hearing loss is a complex and multifaceted condition that can have a significant impact on your quality of life. By understanding the types, causes, and prevention strategies for hearing loss, you can take proactive steps to protect your hearing health and seek appropriate treatment when needed.
If you or a loved one are experiencing hearing loss, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or audiologist for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference in managing hearing loss effectively and improving your overall well-being.
Remember, your hearing health matters, and taking care of your ears is an investment in your future. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your hearing health today for a brighter tomorrow.
If want to know more about hearing loss please visit Medscape.
If you are hearing loss disabled and need support from us please contact us.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.